Nick's Corner
.jpg)
Biomedical Engineering Student | Medical Devices & Bionic Prosthesis Enthusiast
Breast Invasive Carcinoma Research Project
Background and Overview
This study investigates the genetic and clinical characteristics of breast cancer, focusing on mutations within BRCA genes. Utilizing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), the research employs unsupervised learning to identify highly transcribed genes and to analyze factors affecting patient survival outcomes. Key insights are gained into pathways critical for tumor growth, such as cell cycle regulation and NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. This page outlines the study's findings, methodology, and clinical implications for targeted breast cancer therapies.
1.0 Study Objectives
The primary aim of this study was to analyze BRCA gene alterations in breast cancer patients to:
- Identify frequently mutated genes.
- Examine the impact of these genes on biochemical pathways.
- Determine patient demographic characteristics influencing survival.
- Explore possible therapeutic targets through pathway dysregulation insights.
2.0 Methodology
2.1 Data Collection and Preprocessing
Three TCGA datasets (mutation, clinical, and RNA sequencing data) were utilized, with preprocessing to filter for high-impact mutations. Data analysis steps included:
- Kaplan-Meier Survival Analysis: To assess survival based on patient demographics.
- Mutation Analysis: Examining mutation frequencies, oncoplot generation, and clustering.
- Differential Expression Analysis: Using RNA sequencing data to detect key gene expressions across clusters.
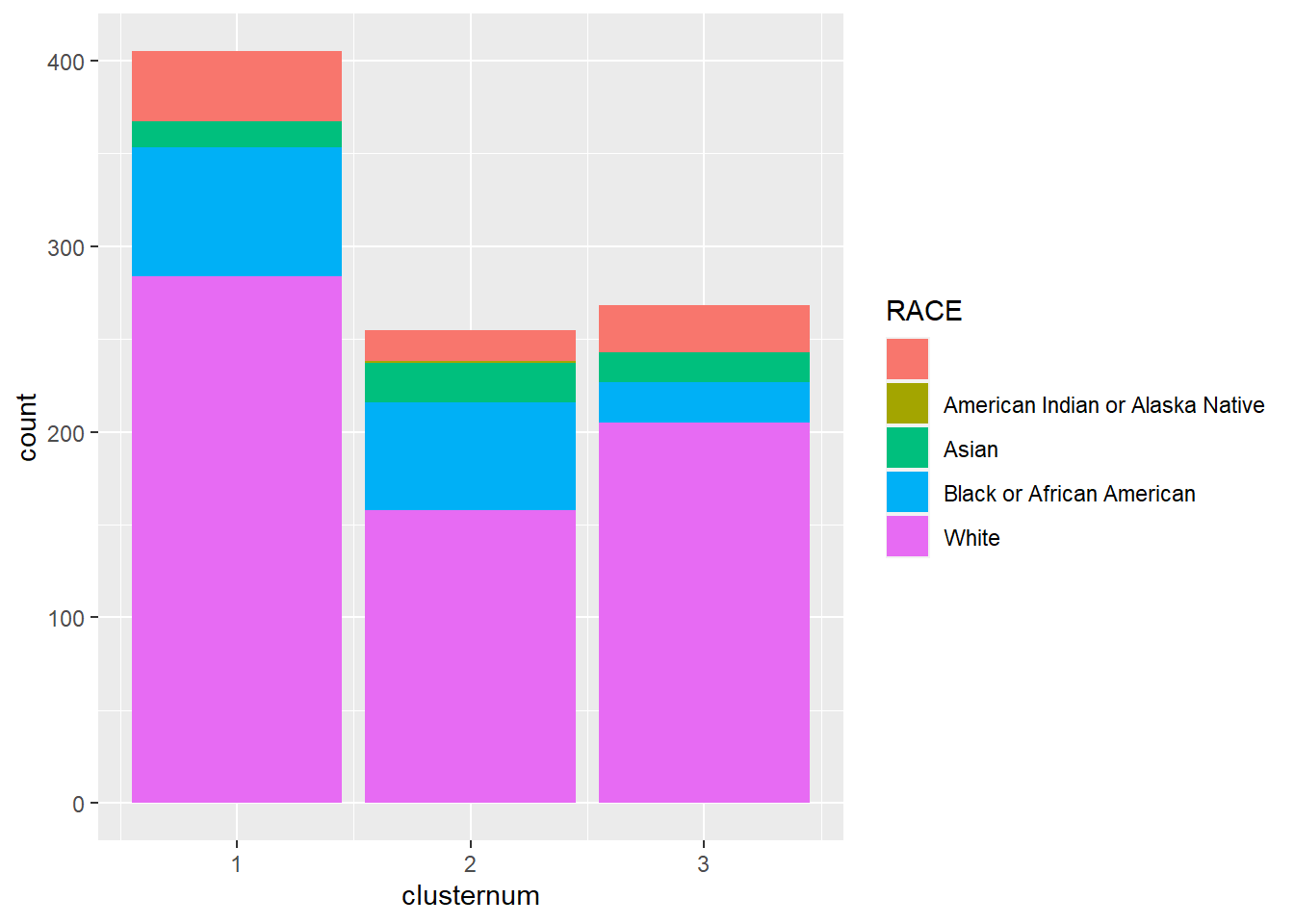
2.2 Clustering and Pathway Analysis
Data was clustered into four groups based on mutation profiles. The clusters were compared for demographic, clinical, and pathway characteristics, with differential pathway expression mapped to identify distinct patterns across clusters.
3.0 Results
3.1 Clinical Summary
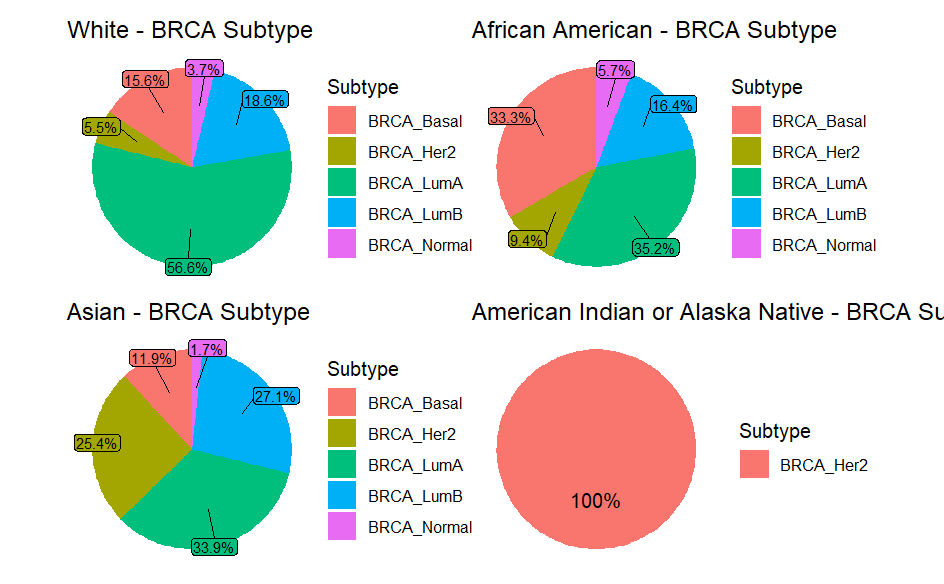
- Patient Demographics: Most patients were White females, with variations across subtypes.
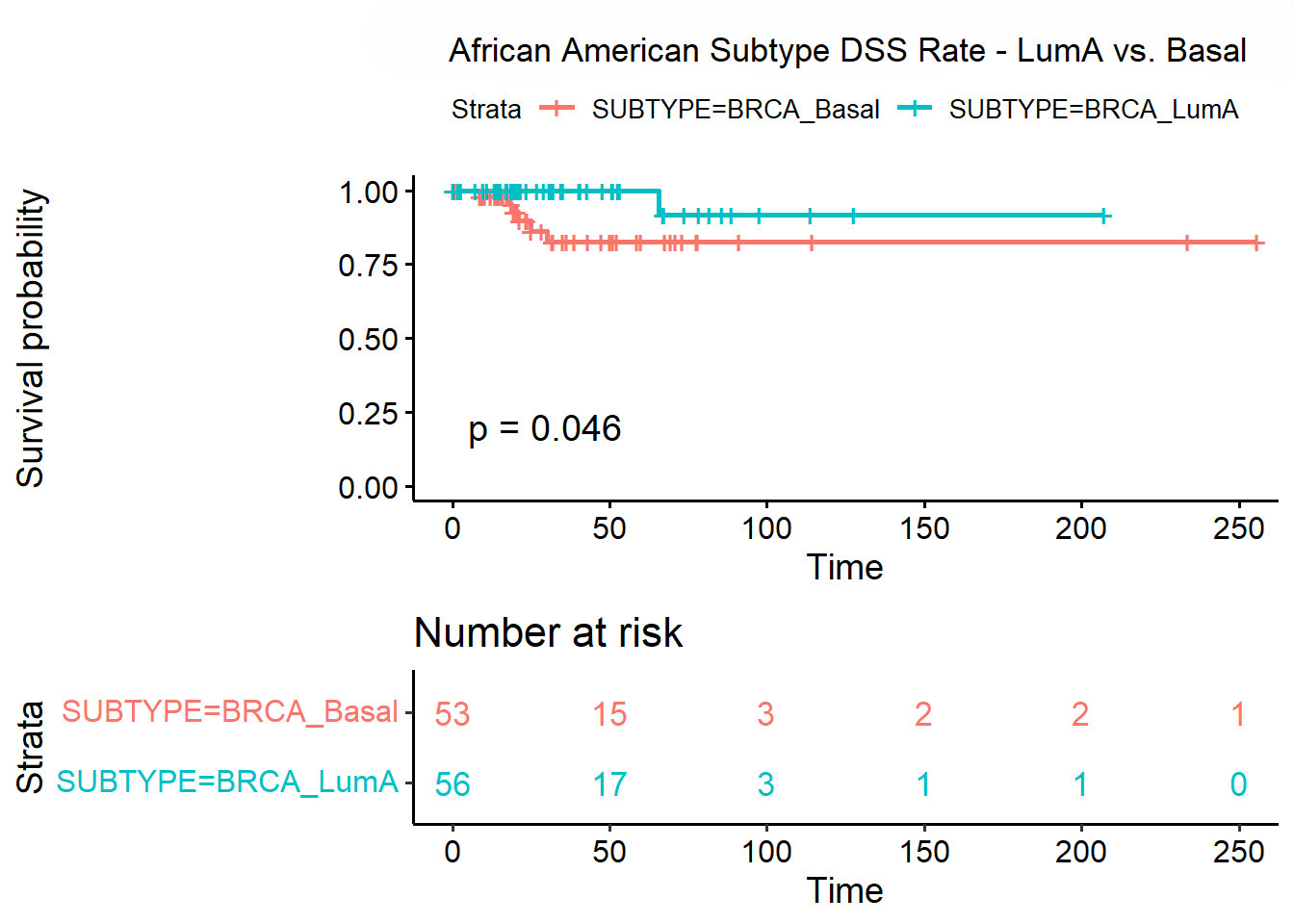
- Survival Outcomes: Differences in survival among subtypes were significant, particularly in African American patients with the Basal subtype.
3.2 Mutation Analysis
Frequent mutations were found in the PIK3CA, TP53, and TTN genes, with missense mutations most common. An oncoplot highlighted four mutation-based clusters, showing gene variation patterns among patient subgroups.
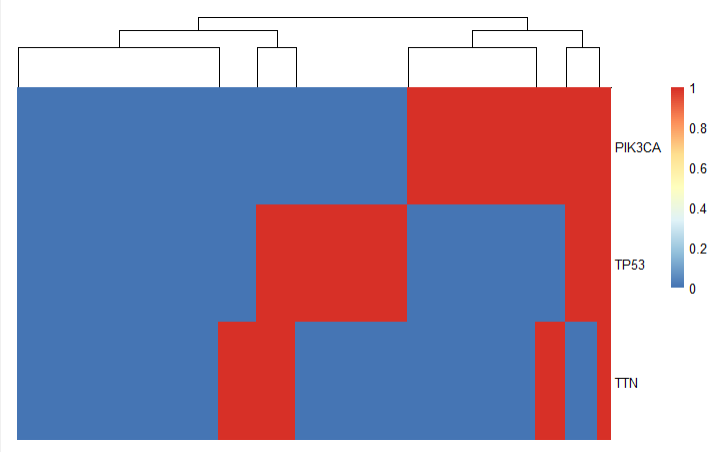
3.3 Pathway Findings
Top pathways affected by gene mutations included:
- Cell Cycle: Downregulated in certain clusters, reflecting impact on cancer progression.
- NK Cell Cytotoxicity: Differentially expressed in clusters, particularly relevant for immunotherapy approaches.
- Antigen Processing: Linked to immune response and potential therapy targets.
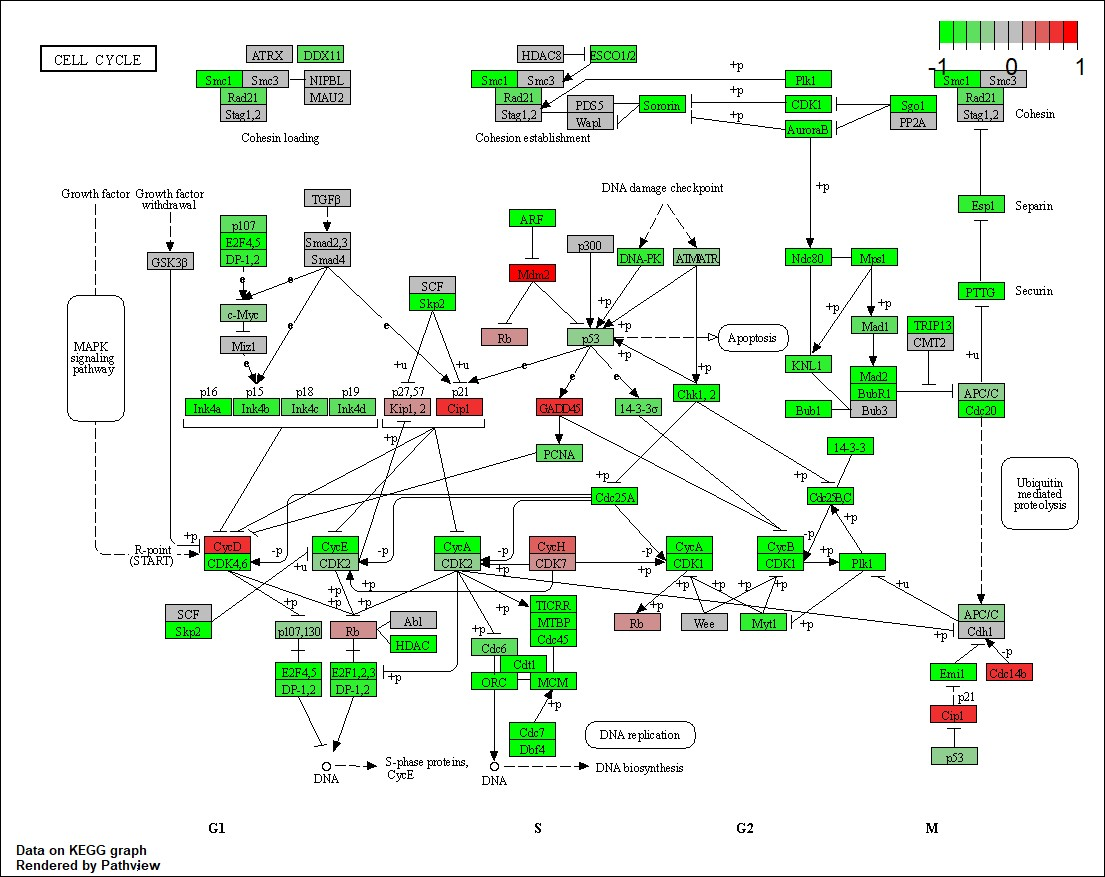
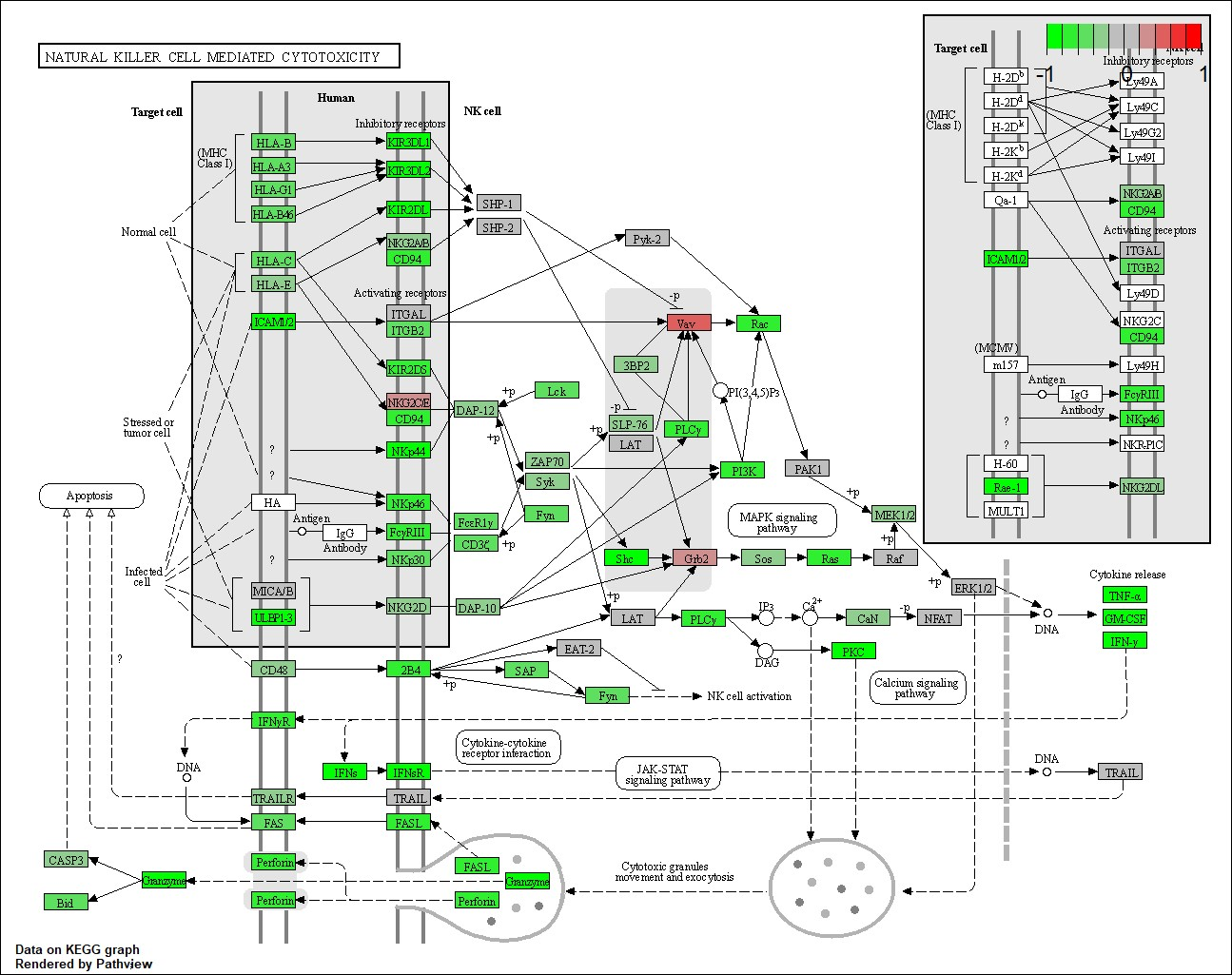
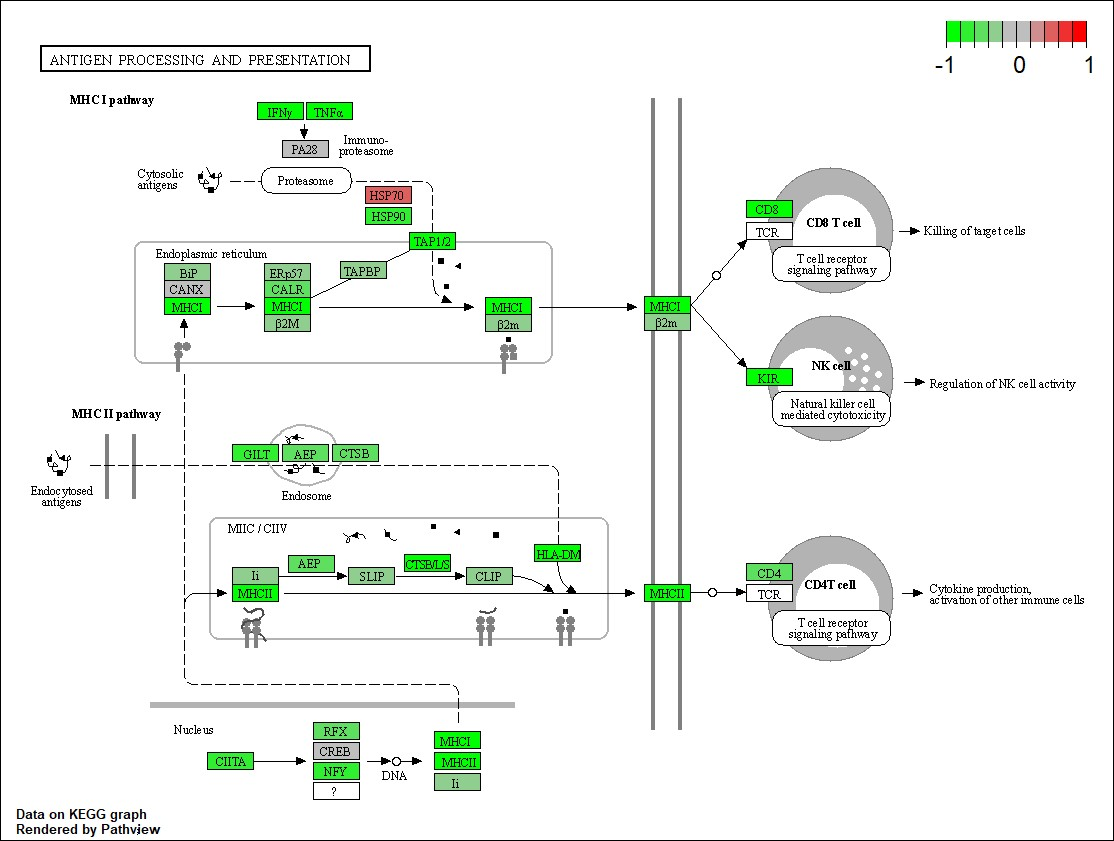
4.0 Discussion
- Demographic Patterns: Differences in BRCA subtypes across ethnic groups align with existing literature.
- Therapeutic Implications: Pathways such as NK cytotoxicity and cell adhesion molecules are potential therapeutic targets, with differential expression suggesting varied responses based on subtype.
5.0 Limitations
The study's hierarchical clustering method faced challenges due to overlapping gene activity across breast cancer subtypes. Improved clustering techniques are recommended for future studies to enhance data segmentation and pathway mapping.
6.0 Conclusion
This study provides valuable insights into the genetic landscape of breast cancer, identifying critical pathways for therapeutic intervention. Future research should focus on refining clustering methods and exploring targeted therapies based on pathway dysregulation.
Download our full report

